Cooperative Society
Definition
A co-operative is an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly-owned and democratically-controlled enterprise.
(Source: International Cooperative Allianceduring 100th cooperative convention in 1994 held in Manchester, London)
Cooperative Values
- Democracy
- Self-responsibility
- Self-help
- Equality and equity
- Solidarity
- Transparency and honesty
Principles of Cooperative
1. Voluntary and open membership
- Voluntary organizations
- Open to all persons able to use their services and willing to accept responsibilites of membership
- Ensuring membership does not have any gender, social, racial, political or religious discrimination
2. Democratic Member Control
- Democratic organization controlled by members whom are actively participating in setting their policies and making decisions.
- All members have equal voting rights (one member, one vote) – irrespective of the number of shares holdings.
3. Member Economic Participation
- Members contribute equitably to and democratically control the capital of their co-operative.
4. Autonomy and Independence
- Autonomous, self-help organizations controlled by their members
- When entering into agreements with other organizations, they ensure terms are democratically controlled by their members and maintain their co-operative autonomy
5. Education, Training and Information
- Provides education and training for their members, elected representatives, managers, and employees in order to contribute effectively to the development of their co-operatives.
6. Cooperation Among Cooperatives
- A thriving cooperative are capable of providing good services.
- Active co-operation between cooperatives can enhance achievement of high-quality community development
7. Concern for Community
- While focusing on member needs, co-operatives work for the sustainable development of their communities through policies accepted by their members.
Benefits of Cooperative Society
- Promotes cooperation and mutual help among members
- Members can learn about aspects of business through cooperatives
- Cooperative can foster relationships among its members
- The cooperative store sells all the items that members need
- Cooperative inculcates the habit of thrift among their membership
- Cooperative provides their members with affordable goods and services
- Create social unity among the people
- Improve the standard of livings of its members
- Employment opportunities
- Provide education and knowledge to members
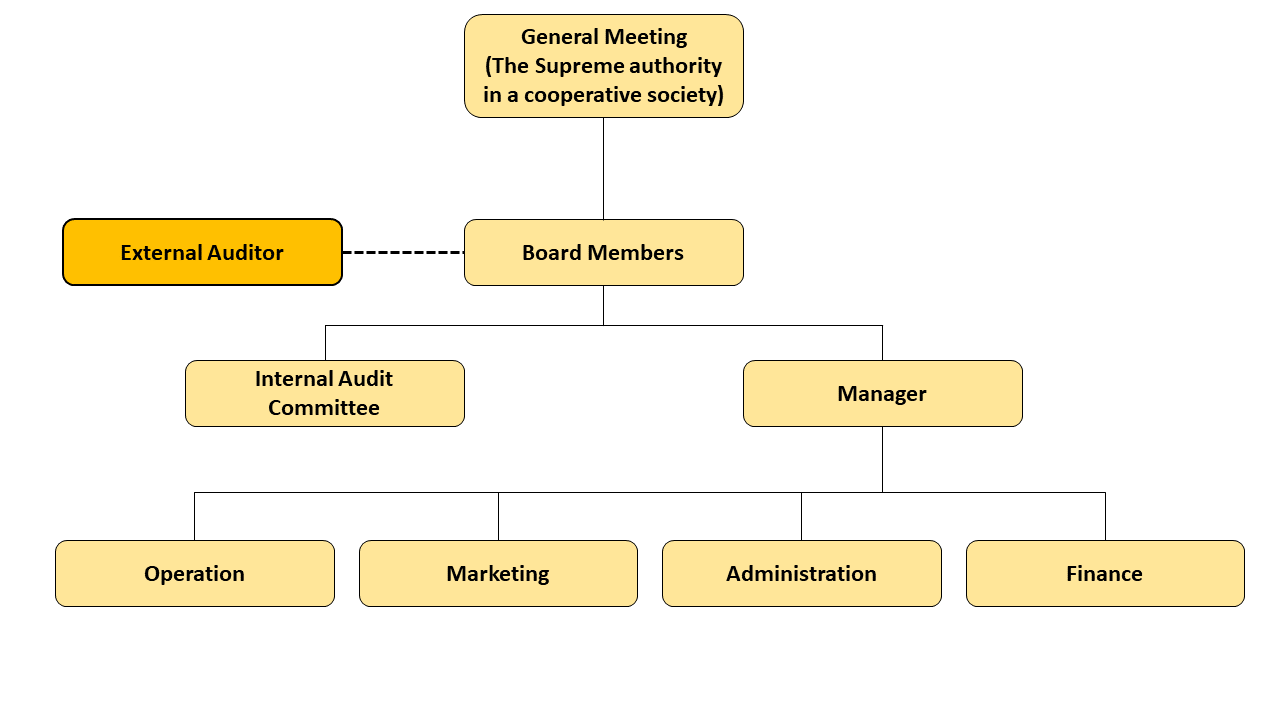
Organizational Structure of a Cooperative

Roles, Duties and Responsibilities of Board Members
The organizational structure of a cooperative is based on democratic principles. Members collectively elect a cooperative’s Board Members from among themselves and the Board Members is responsible for governing the cooperative
Cooperative board members are responsible to ensure the governance of the cooperative society is carried out in accordance with the provisions of the Cooperative Society Act Chapter 84, Rules and By-Laws. Board members shall carry out or execute all decisions agreed upon in the General Meeting in good faith and in a reasonably prudent manner.
Rights and Responsibilities of a Member
Responsibilities of a member
- Pay membership fees
- Acquired a minimum share and shall not hold more than one-fifth (1/5) of the shared capital
- Attend General Meeting
- Provides support to the decision made at the General Meeting
- Loyal to the mutual needs and interests for the success of cooperative activities
Rights of a member
- Voting
- Nominating and electing board members
- Express opinions, views and others
- Benefit financially (Dividend, bonus, etc.) or from services provided by the cooperative
- Using the facilities available in the cooperative
- Be informed about the cooperative
- Receive cooperative education, training and information
Find out more
Cooperative Development Unit,
B19, Spg 32-15
Kg Anggrek Desa,
Bandar Seri Begawan
BB3717
Tel: (673)2383225 / 2383224
